It is crucial to guarantee the safety and quality of food items in the modern, international food sector. Pathogen detection in food is one important component of this, as it is essential to reducing foodborne infections and maintaining public health. Strong food safety regulations, including cutting-edge disease detection methods, are crucial as the food supply chain grows more intricate. The importance of pathogen detection for food safety is examined in this article, along with its effects on public health, techniques, and the function of food testing labs in India in upholding food safety regulations.
Understanding Pathogen Detection in Food
Pathogen detection in food entails locating dangerous microorganisms that can lead to foodborne diseases, such as viruses, germs, and parasites. Among the common pathogens include Norovirus, Salmonella, E. Coli, and Listeria. Food can become contaminated by these germs at any point in the supply chain, from processing and production to packing and delivery. To identify and reduce these hazards and make sure that consumers do not consume tainted food, effective pathogen detection techniques are necessary.
The Impact on Public Health
The importance of pathogen detection in food The effect that safety has on public health is highlighted. Foodborne infections can result in a wide range of serious health problems, from minor gastrointestinal distress to potentially fatal diseases. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that each year, tainted food causes illness in 600 million people, killing 420,000 of them. These figures demonstrate how important it is to have efficient pathogen detection systems in place to stop these kinds of epidemics and safeguard public health.
Methods of Pathogen Detection in Food
There are various methods used for pathogen detection in food, each with its advantages and limitations. These methods can be broadly categorized into traditional and rapid techniques.
Traditional Methods
For many years, conventional approaches, like culture-based procedures, have been utilized to identify viruses in food. These techniques entail cultivating microorganisms on particular media and classifying them according to their traits. Culture-based methods are labor- and time-intensive, frequently taking several days to produce findings, but they are dependable and can provide comprehensive information on the pathogens.
Rapid Methods
Rapid methods for pathogen detection have gained popularity in recent years due to their ability to provide quick and accurate results. These methods include:
1. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): PCR is a molecular technique that amplifies the DNA of pathogens, allowing for their detection in food samples. PCR-based methods are highly sensitive and specific, providing results within hours.
2. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA): ELISA is an immunological method that uses antibodies to detect specific pathogens in food. This technique is widely used due to its simplicity and ability to process multiple samples simultaneously.
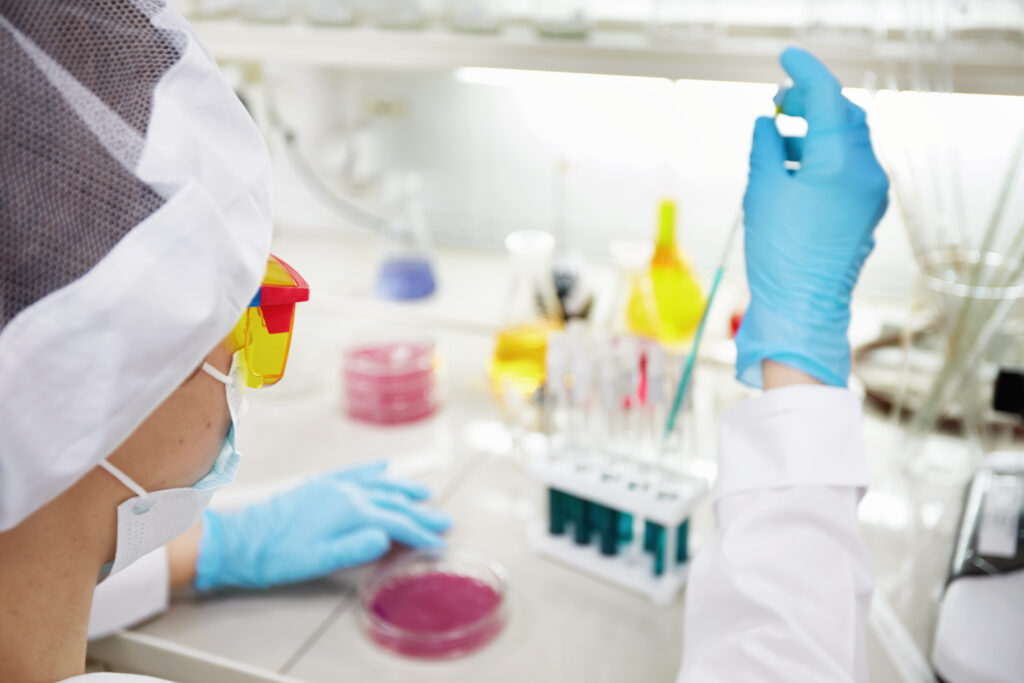

3. Biosensors: Biosensors are devices that use biological molecules to detect pathogens. They offer real-time detection and can be integrated into automated systems for continuous monitoring.
Role of Food Testing Labs in India
Through thorough pathogen detection in food products, food testing labs in India are essential to guaranteeing food safety. These labs are manned by experts who do exact testing to discover pollutants, and they are outfitted with cutting-edge technologies. Beyond simple detection, these labs are important because they offer vital information that aids in identifying the source of contamination and putting preventative measures in place.
India's infrastructure for food testing has advanced significantly, with many recognized labs providing a broad range of testing services. These labs guarantee consistent and dependable testing procedures by adhering to worldwide norms and rules. Food testing facilities in India can detect diseases with great efficiency and accuracy by utilizing cutting-edge technologies, protecting public health.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance
The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is in charge of overseeing the legal framework for food safety in India. To make sure that their products are safe for consumption, food manufacturers must adhere to strict rules imposed by the FSSAI. Adherence to these regulations is crucial, and periodic inspections and audits are carried out to verify compliance.
One important aspect of these regulatory regulations is the detection of pathogens in food. To identify and remove viruses from their products, food manufacturers need to put strong testing methods in place. Serious consequences, such as product recalls and legal action, may arise from breaking these standards. Consequently, making investments in trustworthy pathogen detection techniques is not only required by law but also essential to preserving customer confidence and brand reputation.
Conclusion
The importance of pathogen detection in food safety cannot be overstated Effective disease detection techniques are becoming more and more important as the world's food supply chain gets more intricate. We can protect consumers' safety and well-being by preventing foodborne illnesses and reducing the dangers posed by dangerous germs.
Indian food testing labs are essential to this effort since they use cutting-edge technology to deliver precise and trustworthy disease detection services. Upholding strict food safety regulations requires constant innovation in testing procedures and compliance with regulations.
Improving pathogen detection in food will require the future integration of state-of-the-art technologies and cooperative efforts among stakeholders. Prioritizing food safety and making significant investments in reliable detection systems will help us create a safer and better